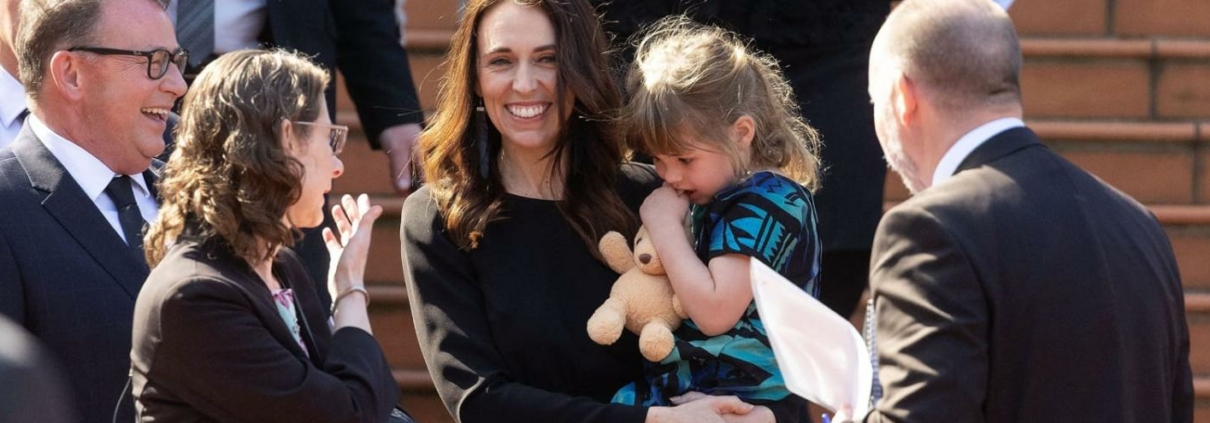
Jacinda Ardern was only 37 when she became Prime Minister of New Zealand. A working mother, she smashed the glass ceiling. After five tumultuous years, she stepped aside with a simple message: “The decent traits of a human being should be the decent traits of leaders.” Her words are in sharp contrast to the behavior of many current leaders.
Leadership is not about personality; it’s about behavior. That lesson carries forward from the Torah to leaders like Ardern. At Parshat Emor, the Torah sets out the rules of behavior expected of High Priests. Priests follow rules that elevate their status. They should not be exposed to the dead, must remain scrupulous in their relationships, and stay meticulous in their duties. Looking past the particulars of temple sacrifice or the limitations on marital relations, the message is clear, leadership’s behavior sets a standard for all of us.
Ardern reflected on her tenure in 2023: “The most important leadership principles can be found in what we teach our children — empathy, curiosity, bravery, and kindness.” Great leaders should have these traits in the 21st century.
Soon after becoming Prime Minister, crisis tested Arden’s leadership. In 2019, a white nationalist live-streamed his attacks on two mosques in Christchurch. Fifty-one people died. Ardern’s response was exemplary.  Within two days of her demand, the parliament banned semi-automatic weapons. Describing the victims, most of whom were immigrants to New Zealand, Ardern said: “They are us. The person who has perpetuated this violence against us is not. They have no place in New Zealand.” Ardern later remarked that “the characteristics we should necessarily deploy in troubled times are defined by the kind of humanity” we should always bring to leadership.
Within two days of her demand, the parliament banned semi-automatic weapons. Describing the victims, most of whom were immigrants to New Zealand, Ardern said: “They are us. The person who has perpetuated this violence against us is not. They have no place in New Zealand.” Ardern later remarked that “the characteristics we should necessarily deploy in troubled times are defined by the kind of humanity” we should always bring to leadership.
Ardern’s legacy challenges all leaders, especially in the United States. Americans must hold their leaders to the same standards of behavior as Ardern. If your people are hurting, hurt with them. Protect threatened minorities. People who are militant and ethno-nationalist have no place in civilized society. Similarly, the new antisemitism of the intersectional left is equally hateful and underserving of space on campus or in political realms.
America needs leaders who appeal to our overarching goals as a nation of immigrants, ensuring freedom, security, and opportunity for everyone. This country’s journey must reflect these high ideals, encourage hope, and pursue standards of excellent behavior.
In an election year, we need Arden’s reminder: how leaders behave reflects the purpose of their position. In a time of petulant and egoistic politicians, Jacinda Ardern’s words seem prophetic. We should select leaders who cherish decency displayed by their behaviors – “empathy, curiosity, bravery, and kindness.” Leaders’ willingness to adhere to standards of proper behavior truly sets the standard for us all.
Rabbi Evan J. Krame












 Evan J. Krame was ordained as a rabbi by the
Evan J. Krame was ordained as a rabbi by the